What is Ajax?
AJAX stands for Asynchronous JavaScript And XML. In a nutshell, it is the use of the XMLHttpRequest object to communicate with servers. It can send and receive information in various formats, including JSON, XML, HTML, and text files. AJAX’s most appealing characteristic is its “asynchronous” nature, which means it can communicate with the server, exchange data, and update the page without having to refresh the page.
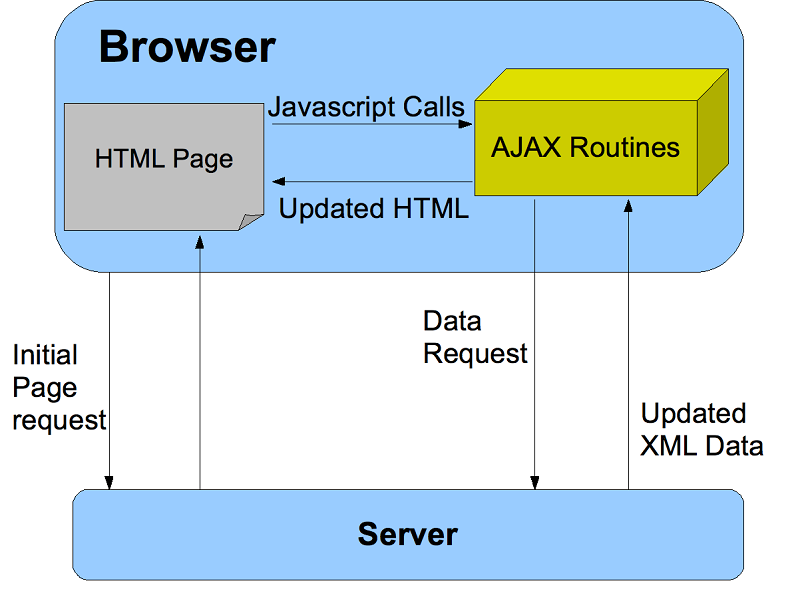
https://systemoutofmemory.com/blogs/the-programmer-blog/javascript-understanding-ajax-calls
Why shoud we use Ajax?
- Make requests to the server without reloading the page.
- Receive and work with data from the server.
Fetch API
Fetch provides a generic definition of Request and Response objects (and other things involved with network requests). This will allow them to be used wherever they are needed in the future, whether it’s for service workers, Cache API, and other similar things that handle or modify requests and responses, or any kind of use case that might require you to generate your responses programmatically (that is, the use of computer program or personal programming instructions).
fetch() vs jQuery.ajax()
- The Promise returned from fetch() won’t reject on HTTP error status even if the response is an HTTP 404 or 500. Instead, as soon as the server responds with headers, the Promise will resolve normally (with the ok property of the response set to false if the response isn’t in the range 200–299), and it will only reject on network failure or if anything prevented the request from completing.
- fetch() won’t send cross-origin cookies unless you set the credentials init option.
Example
const myImage = document.querySelector('img');
let myRequest = new Request('flowers.jpg');
fetch(myRequest)
.then(function (response) {
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP error! status: ${response.status}`);
}
return response.blob();
})
.then(function (response) {
let objectURL = URL.createObjectURL(response);
myImage.src = objectURL;
});